When Chocolate Need Tempering
Tempering is the final step in production and has a major impact on the final chocolate experience for consumers. Have you ever had a chocolate bar that was crumbly and had an opaque white film on the outside? Either the tempering wasn’t done right or something was wrong with the ingredients
To understand the root of this problem, you need to know a little about the fat in chocolate. Cocoa butter accounts for 48%-57% of the weight of cocoa beans. It is the substance that makes chocolate insoluble in the hand (solid at room temperature) only soluble in the mouth (begins to melt at body temperature). Putting a piece of chocolate on your tongue and feeling it slowly melt in your mouth is one of the most seductive qualities of chocolate, all thanks to cocoa butter.
Cocoa butter is polymorphic, which means that, under different solidification conditions, it forms different types of crystals, which can be either stable or unstable. Stable crystals are closely packed and have higher melting points than unstable crystals. We have to temper the chocolate properly so that when you taste it it is still as smooth on the outside and soft on the inside as we made it.
Cocoa butter is a polymorph, which is identified as having 5 different crystal forms 1, y (Gamma) type, which is formed by rapid cooling at low temperature. It is an extremely unstable crystal form, and its melting point is about 17°C2 , a (Alpha) type, y type can quickly evolve into a type, its melting point is between 21~24°C, but it slowly changes into B’ crystal form 3, B’ (Beta-prime), it has B’1 and B’2 two crystal forms, the melting point of B’2 crystal form is between 27 and 29°C.
4. Bi crystal form, its melting point is about 33C. Form B’ slowly transforms to Form B
Form B is the most stable crystal form, and its melting point is about 34 ~ 35°C.
In addition, some people believe that cocoa butter crystals have 6 crystal forms, represented by numbers 1~6, and the melting points of these 6 types are: 173 23 3% 25 5% 265% 33 836.4°. Crystal forms 1 to 4 are basically the same as 1 to 4 of the above five crystal forms, and they are all unstable crystal forms. The difference is that the fifth crystal form B is the most stable crystal form with normal temperature regulation. will slowly transform into the more stable sixth crystal form.
Tempering is to ensure that cocoa butter and cocoa butter-like form the most stable crystal form, and then cool it correctly so that the chocolate has a good luster and no whitening phenomenon for a long time.
Usually the method of tempering chocolate includes the following steps
1. Melt the chocolate completely
2. Cool to the crystallization temperature point
3. Produce crystallization
4. Melt away unstable crystals
Melanger
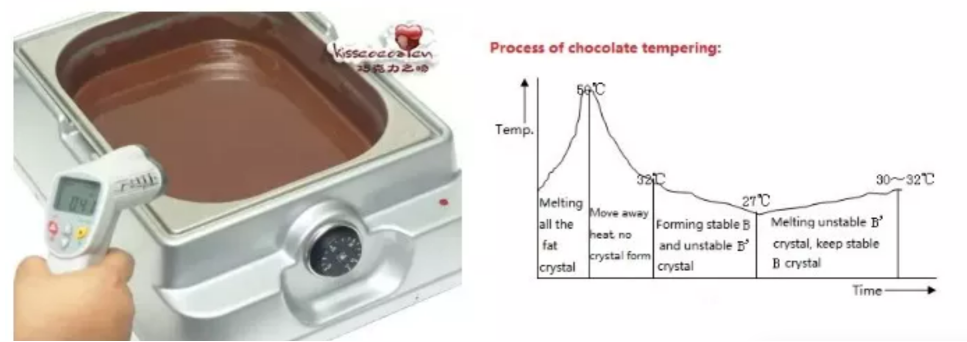
In the tempering stage, the chocolate is heated, cooled and then gently reheated to a precise temperature to obtain stable crystals of cocoa butter. In this way, you can get a smooth and shiny appearance when it solidifies, and the mouthfeel is just right, and you can still hear the crisp sound when you break the chocolate bar.
In actual production, the temperature of the refined chocolate is generally above 45, and the temperature of the chocolate kept warm in the insulation tank is also between 40 and 45, and there is no crystallization of any fat. Therefore, the first stage of tempering is to remove the sensitive heat that affects the crystallization of fat, that is, to cool the chocolate mass from 40 to 50 to 32 by cooling. In the second stage of temperature regulation, the material continues to cool from 32° to about 27°C, and the oil begins to form stable B crystal form and unstable B” crystal form. The third stage of temperature regulation is the last stage of temperature regulation, also known as In the temperature recovery stage, the material temperature rises from 27 to 30 ~ 32. The purpose of recovery is to melt the unstable B crystal form repeatedly by heating, leaving the most stable B crystal form.
The temperature can be adjusted manually, but the temperature must be accurate. Choosing a chocolate tempering machine that precisely controls the temperature to a temperature difference of less than ±0.2 can help you very well. The tempering of different chocolates is also completely inconsistent: